
With these ideas in mind, the main objectives of the blockade were to prevent desperately needed goods-including war material, manufactured goods, and luxury items-from reaching the South and to stop the exportation of raw cotton to foreign manufacturers.Īccomplishing these objectives in 1861 proved to be a challenge because the Union Navy at the beginning of the war had only thirty-five modern vessels (only three of which were steam powered) to patrol 189 harbors and 3,000 miles of coast. In addition, the South relied on them to purchase Southern cotton and other cash crops. Scott knew that the South relied heavily on manufactured goods from the Northern states and foreign countries. Starting on April 19, 1861, the blockade was part of General Winfield Scott's strategy called the Anaconda Plan, which was an effort to reduce the South's ability to make war. However, it did seriously weaken the ability of the states in rebellion to fight and, in combination with Lincoln’s plan to pursue a land war, led to the defeat of the South.The first action of naval warfare in the American Civil War was the blockade of Southern ports by the Union Navy. In actual practice, Winfield Scott’s Anaconda Plan did not bring an early end to the war as he had hoped. Why was the Anaconda Plan not successful? It included blockading Southern coasts and securing control of the Mississippi River. It was called the Anaconda Plan as it would strangle the Confederacy by cutting it off from external markets and sources of material.

Union General Winfield Scott proposed a plan to achieve a Northern victory.
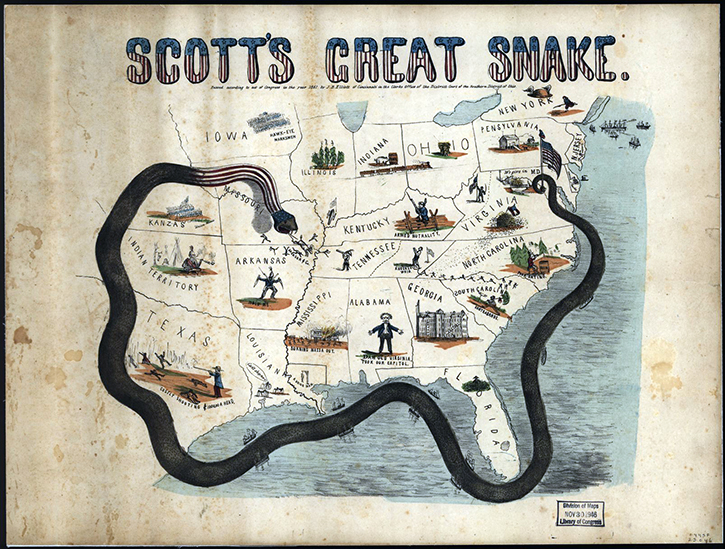
Scott came up with the plan in early 1861, intending it as a way to end the rebellion predominantly through economic measures What was the Anaconda Plan in the Civil War? Army to put down the rebellion by the Confederacy in 1861.
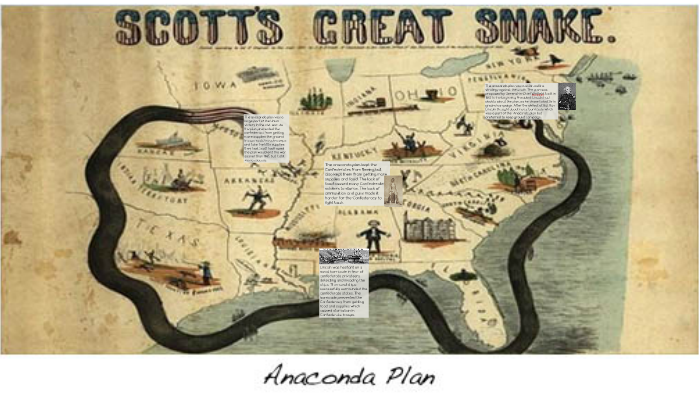
The Anaconda Plan was the initial Civil War strategy devised by General Winfield Scott of the U.S. Like the coils of an anaconda snake suffocating its victim, the south would be squeezed until it returned to the Union. Then an advance down the Mississippi River was to cut the South in two. The plan called for the blockade of the Southern ports. It was proposed by General Winfield Scott. Blockading fleets were also used on inland rivers to assist Union military operations. Scott’s Great Snake, published at the outset of the Civil War, humorously portrays General Winfield Scott’s Anaconda Plan to strangle the southern states by cutting off any imported supplies and halting cotton exports. What is the Anaconda Plan in the Civil War? This would cut off and isolate the south from the outside world. The goal was to defeat the rebellion by blockading southern ports and controlling the Mississippi river.

The Anaconda Plan was the Union’s strategic plan to defeat the Confederacy at the start of the American Civil War. Although about 90 percent of Confederate ships were able to break through the blockade in 1861, this figure was cut to less than 15 percent a year later What was the reason of the Anaconda Plan? Ridiculed in the press as the Anaconda Plan, after the South American snake that crushes its prey to death, this strategy ultimately proved successful. What was the result of the Anaconda Plan? Prize law is that part of international law which concerns the capture of enemy property by a belligerent at sea during war. In less than a week, the Union began its blockade of the southern states in an effort to prevent the trade of goods, supplies, and weapons between the Confederacy and other nations. Scott came up with the plan in early 1861, intending it as a way to end the rebellion predominantly through economic measures What was the purpose of the blockade by the union? The plan called for a naval blockade of the Confederate littoral, a thrust down the Mississippi, and the strangulation of the South by Union land and naval forces Why did the union use the Anaconda Plan? What was the purpose of the Anaconda blockade?Īnaconda plan, military strategy proposed by Union General Winfield Scott early in the American Civil War.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
